gravimetric determination of water of crystallization by volatilization method|volatilization gravimetry chemistry : supermarket We can also use the results from volatilization gravimetry analysis to determine the percentage of water of crystallization. The percentage of water of crystallization tells us the . web26 de jan. de 2023 · "Não podia mais oprimir quem eu era de verdade", relata Juana Ocio sobre quando se assumiu trans. Ma Zink, Juana Ocio, Miles Espadoto, Stefan Costa e .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB39K Followers, 373 Following, 124 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from ThaisOliveira (@thaisoliveiraoficiall)
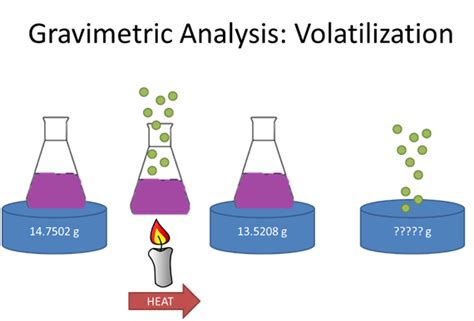
The best way to appreciate the theoretical and practical details discussed in this section is to carefully examine a typical volatilization gravimetric method. Although each method is unique, the determination of Si in ores and alloys by forming volatile SiF 4 .The best way to appreciate the theoretical and practical details discussed in this . We can also use the results from volatilization gravimetry analysis to determine the percentage of water of crystallization. The percentage of water of crystallization tells us the .
Common gravimetric methods based on volatilization for determining water and carbon dioxide. Quantitative distillation of water from products by heating. Direct determination .Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative determination of the amount of analyte through a precipitation process, precipitate isolation, and determination of isolated product weight.The change in the absorbent’s mass provides a direct determination of the amount of water in the sample. An easier approach is to weigh the sample of food before and after heating, using .
In this lesson, we will learn how to use volatilization gravimetry to calculate the quantity of analyte in a sample or determine the formula of a hydrated compound.We can determine the mass of water of crystallization in a salt, such as this, using volatilization gravimetry. If we know the mass of the hydrated salt and we remove the water of crystallization using thermal energy by heating, the water will escape as a vapor leaving behind a white powder.
A second approach to gravimetry is to thermally or chemically decompose the sample and measure the resulting change in its mass. Alternatively, we can trap and weigh a .The best way to appreciate the theoretical and practical details discussed in this section is to carefully examine a typical volatilization gravimetric method. Although each method is unique, the determination of Si in ores and alloys .Classifying Quantitative Analytical Methods • Gravimetric Methods: Determine the mass of the analyte or some compound chemically related to it. Analyte: the compound or species to be .
volatilization gravimetry chemistry
Thermogravimetry. One method for determining the products of a thermal decomposition is to monitor the sample’s mass as a function of temperature, a process called thermogravimetry.Figure 8.3.1 shows a typical thermogram in which each change in mass—each “step” in the thermogram—represents the loss of a volatile product. As the following example . Gravimetric analysis is an analytical technique used for the quantitative determination of an analyte based on the mass of a solid. . The analytical technique of gravimetric volatilization separates the masses using .Indirect method volatilization gravimetry. In indirect methods we can define weight of the rest of substance after full removal of a defined volatile component. It is used for moisture determination or to find water of crystallization, etc. %( ) 1 2 100%; a m m Z A m 1 –mass of the sample before drying m 2 –mass of the sample after drying Method 925.10 in Official Methods of Analysis, 18th Edition (AOAC International, 2007) provides an approved method for determining the moisture content of flour. A preweighed sample is heated for one hour in a 130 o C oven and transferred to a desiccator while it cools to room temperature.
ex: in Ag+ analysis, primary adsorbed ion : Cl- washing with an acidic soln → counter-ion layer : H+ → HCl volatilized when ppt is dried c. Reprecipitation, double precipitation 2. Mixed-crystal formation a contaminant ion replaces an ion in the lattice of a crystal a. the same charge b. the size differ < 5 % c. salt : the same crystal classdefine the volatilization method in gravimetric analysis, describe the experimental procedure involved in volatilization gravimetry, connect the loss of mass of a hydrated compound with the loss of water molecules from the compound, calculate the percentage of water of crystallization in a hydrated compound,
12A-1 Properties of Precipitates and Precipitating Reagents A gravimetric precipitating agent should react specifically or at least selectively with the analyte and give precipitates that is: 1. Enough particle size for retaining on filter paper 2. High purity (free of contaminants) 3. Low solubility that no significant loss of the analyte occurs during filtration
The simple gravimetric analysis involves simple heating, precipitation, drying and separation of sample in order to find out volatile and non-volatile components. The analyte may be separated from the sample by converting it into gas and the mass of gas serves as measure of analyte concentration this process is known as volatilization .The precipitation method is the one used for the determination of the amount of calcium in water. Using this method, an excess of oxalic acid, H 2 C 2 O 4, is added to a measured, known volume of water.By adding a reagent, here ammonium oxalate, the calcium will precipitate as calcium oxalate.The proper reagent, when added to aqueous solution, will produce highly . 4. Types of Gravimetric Analyses: • There are two main types of gravimetric analyses: A) Precipitation – analyte must first be converted to a solid (precipitate) by precipitation with an appropriate reagent. The precipitates from solution is filtered, washed, purified (if necessary) and weighed. B) Volatilization – In this method the analyte or its decomposition .
Precipitation and volatilization gravimetric methods require that the analyte, or some other species in the sample, participate in a chemical reaction. . Particulate gravimetry is important in the environmental analysis of water, air, and soil samples. . Except for methods relying on a quartz crystal microbalance, particulate gravimetry . Because the release of a volatile species is an essential part of these methods, we classify them collectively as volatilization gravimetric methods of analysis. 8.4: Particulate Gravimetry Precipitation and volatilization gravimetric methods require that the analyte, or some other species in the sample, participates in a chemical reaction.
Gravimetric Methods Chapter Overview 8A Overview of Gravimetric Methods 8B Precipitation Gravimetry 8C Volatilization Gravimetry 8D Particulate Gravimetry 8E Key Terms 8F Chapter Summary . The change in the absorbent’s mass provides a direct determination of the amount of water in the sample. An easier approach is to weigh the sample ofDetermination of Water of crystallization in copper sulphate hydrous CuSO4.XH2O using Volatilization method Theory: Water of crystallization is the water forming part of crystal structure of certain materials, known as crystalline hydrate. The contents of .
volatilization gravimeter thermogram
What is Gravimetric Analysis? Gravimetric analysis is a method in analytical chemistry to determine the quantity of an analyte based on the mass of a solid. Example: Measuring the solids suspended in the water sample – Once a .It is a crucial method within gravimetric analysis, complementing other techniques like volatilization gravimetry. Solubility Product : The solubility product (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that represents the extent to which a sparingly soluble .• Indirect analyses based on the weight of the residue remaining after volatilization are commonly used in determining moisture Cont’ • Organic analysis –the combustion products are passed through preweighed tubes .Volatilization method • In this method the analyte or its decomposition . • Example, Water can be separated from most inorganic . compounds by ignition. . Gravimetric analysis avoids problems with temperature fluctuations, calibration errors, and other problems associated with .
Gravimetry is a method of quantitative chemical analysis. It qualifies as a macroscopic quantitative method of analysis because it involves relatively important quantities of a substance to be determined compared to more recent methods, such as electrochemical, spectroscopic, and chromatographic means.Ask the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question gravimetric analysis, a method of quantitative chemical analysis in which the constituent sought is converted into a substance (of known composition) that can be separated from the sample and weighed. The steps commonly followed in gravimetric analysis are (1) preparation of a solution containing a known weight of . Gravimetric Methods and Volatilization. Common gravimetric methods based on volatilization for determining water and carbon dioxide. Quantitative distillation of water from products by heating. Direct determination of water by collecting it on a solid desiccant. Indirect determination of water by measuring the loss of mass in the sample during .
Elemental weight can be calculated based on the formula of the compound and the atomic weight of the element the elements or compounds contained in it are carried out in various ways, such as . A variant of the hygroscopic gravimetric technique is developed for the estimation of the total content of soluble impurities in solid crystalline chemical reagents, by considering water vapor sorption from an atmosphere with a definite relative humidity. The technique makes it possible to estimate the main component content of a substance, provided this substance is .A {eq}4.256 g {/eq} sample of the commercial product was heated strongly to drive off the waters of crystallization. The anhydrous residue weighed {eq}2.256 g {/eq}. Volatilization Gravimetry Analytical Technique Mass Measurement Volatile Material Sample Analysis High Temperature Crucible Non-volatile Components Concentration Calculation Water Of Crystallization Chemical Reagent Treatment Selective Absorption Carbonate-containing Compounds Soda-lime Absorption NaOH Trapping.
Gravimetric analysis is based on the measurement of the mass of a substance of known composition that is chemically related to the analyte. Gravimetric analysis includes precipitation, volatilization and electrodeposition methods. In precipitation gravimetry of the analyte is carried out by the use of inorganic or organic Before we consider specific gravimetric methods, let’s take a moment to develop a broad survey of gravimetry. . Method 925.10 in Official Methods of Analysis, 18th Edition (AOAC International, 2007) . we call the method volatilization gravimetry. In determining the moisture content of bread, for example, we use thermal energy to vaporize .
continental aircraft engine compression test
continental compression test
web🇧🇷. Stream. 23 Episódios HD. We checked for updates on 68 streaming services on 17 de fevereiro de 2024 at 11:04:52. Problemas de relatório. Assistir Arquivo Morto Temporada .
gravimetric determination of water of crystallization by volatilization method|volatilization gravimetry chemistry